Shaping the future
How the future will look at Audi is presented in a clearly detailed vision: The company aims to be carbon-neutral on balance1 by 2050. On the way to achieving this target, every phase of a vehicle’s life cycle is being examined – not just with measures in the manufacturing stage, but also processes that have an effect earlier on, such as in the supply chain. At the heart of it all is a plan to use resources responsibly, consistently reduce carbon emissions, and expand electric mobility. By 2025, Audi wants to reduce the carbon footprint of its fleet along the entire product life cycle by around 30 percent compared with the reference year of 2015. To achieve this, it is increasingly focusing on electric mobility.

An on-balance carbon-neutral¹ future for all Audi plants
The year 2025 is also an important milestone for Audi’s Mission:Zero environmental program, which is committed to achieving greater sustainability across the production network. All Audi plants are set to be carbon-neutral on balance1 by that date. The plants in Brussels and in the Hungarian city of Győr already have on-balance carbon-neutral1 operations. Important components here include the use of geothermal energy – which plays an essential role at Audi Hungary – and the installation of photovoltaic (PV) systems. In Brussels, the PV system occupies an area of around 107,000 square meters. The heat supply for the site in Belgium is covered by certificates for biogas. Audi Brussels is offsetting further emissions that cannot yet be prevented through the use of renewable energy sources by means of carbon credit projects.
Mission:Zero at the Ingolstadt plant
The company’s headquarters is also on its way to becoming an on-balance carbon-neutral1 site: Since the start of 2012, the Audi plant in Ingolstadt has been solely using green electricity to build its automobiles. Photovoltaic modules on an area occupying around 23,000 square meters are providing renewable energy. In addition, external businesses in the surrounding area, including a refinery, are supplying the site with low-carbon waste heat.
Furthermore, a new process water supply center with a membrane bioreactor was commissioned in Ingolstadt in 2019 to turn the wastewater into high-quality industrial water by passing it through a series of cleaning stages, significantly cutting the need for fresh water at the production plant. Audi has also been committed to greater environmental protection since 2009 with the Audi Environmental Foundation.
Initiative
Audi is a member of the Global Battery Alliance – a multi-stakeholder initiative whose aim is to define sustainability along the entire value chain of batteries. Among other things, this alliance focuses on the safeguarding of human rights and social standards when mining the raw materials as well as finding ways of reusing lithium-ion batteries.
Optimizing water consumption
The circular economy principle is also a key aspect in the area of production. This relates to the consumption of water, among other things. The San José Chiapa site in Mexico is demonstrating how the future of the Audi sites could look in this regard, because the site already runs a production operation that generates no wastewater whatsoever. All wastewater is treated and reused at the site.
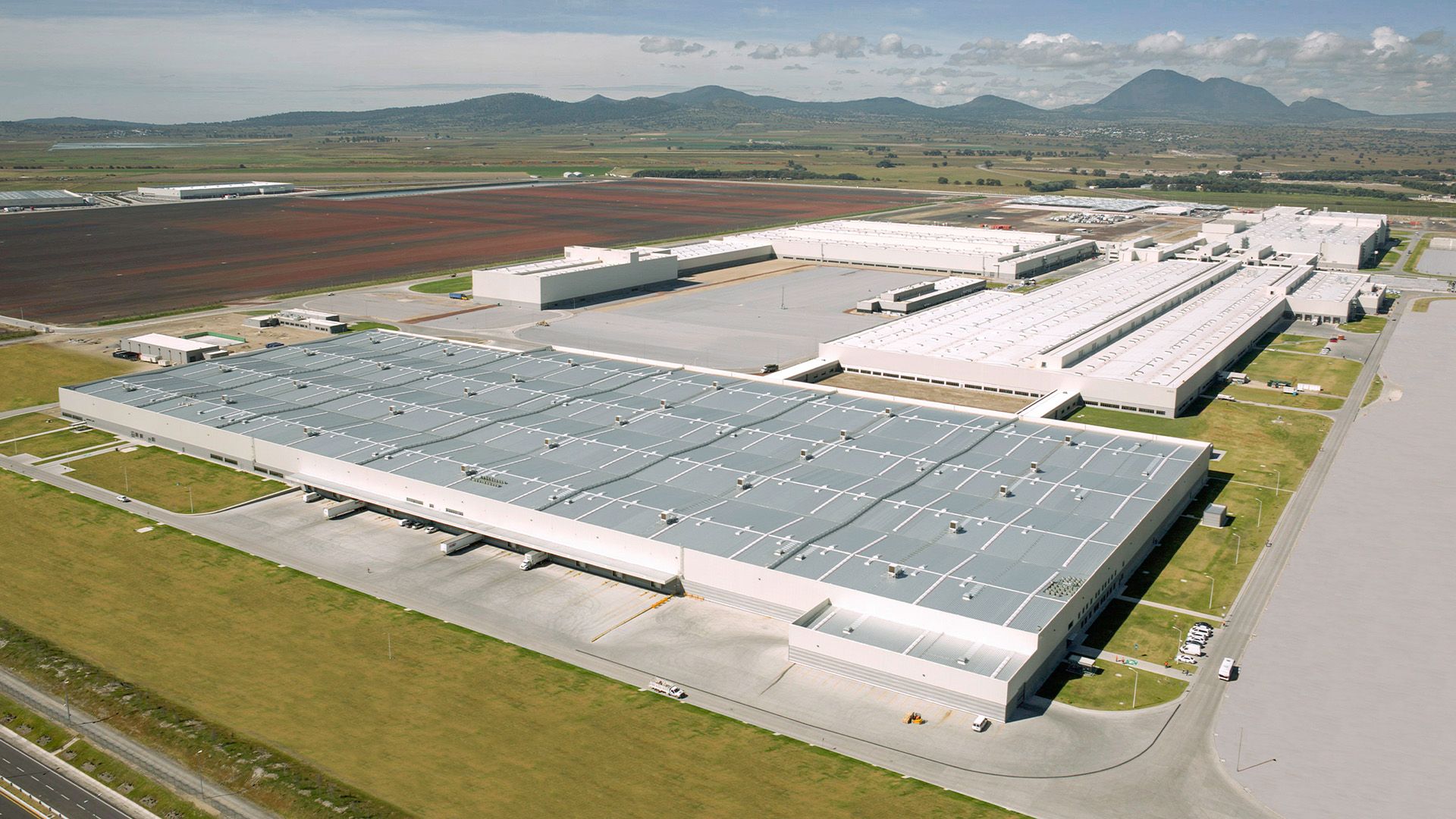

Decarbonizing the supply chains
Audi is also looking toward the future with some smart ideas in the area of the supply chain. The company is engaged in constructive dialogue with relevant suppliers, subcontractors, and partners. As part of the carbon program launched in 2018, joint measures are being developed to reduce carbon emissions. The focus is on aluminum, steel, and battery components, which require a significant amount of energy to produce. Workshops have already resulted in measures along the supply chain that together have the potential to reduce 1.2 tons of carbon emissions across the vehicle fleet. The implementation of the agreed measures is set to be an inherent feature of newly agreed contracts in the future. Since 2018, the use of green electricity has been one of the conditions set out in supply contracts agreed with high-voltage battery manufacturers.
The aluminum closed loop is another of the measures agreed with the suppliers. Behind it is an efficient cycle involving the processing of aluminum sheet metal in the plant: The aluminum sheet offcuts that accumulate in the pressing plant are returned directly to the suppliers, who process them and turn them into new products. The aluminum sheets produced in this manner are then used by Audi again in its production plants. Since introducing this measure in Neckarsulm and Ingolstadt, Audi has been able to cut around 350,000 tons of carbon emissions on balance1. The aluminum closed loop is set to be rolled out to further plants in the future.
Sustainability certificate
Aluminum is used for the housing of the batteries on the Audi e-tron models. The Aluminium Stewardship Initiative (ASI) has awarded Audi its sustainability certificate for the sustainable production of the battery housing (source: aluminium-stewardship.org).
Some see a factory. We see the next level.

Audi e-tron Sportback: Power consumption (combined) in kWh/100 km: 25.9–21.1CO₂ emissions (combined) in g/km: 0CO₂ emission class: A
German model shown. Stated specifications apply only in Germany and are not applicable in other regions.
Audi e-tron Sportback: Power consumption (combined) in kWh/100 km: 25.9–21.1CO₂ emissions (combined) in g/km: 0CO₂ emission class: A
German model shown. Stated specifications apply only in Germany and are not applicable in other regions.




